

Try BLAST+ 2.14.1 today Check out the changes we made. The program compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance. The primary benefit of de novo sequencing over conventional MS-based sequence analysis is that it allows researchers to study proteins and peptides for which there is no reference sequence – antibodies for instance. The Protein database is a collection of sequences from several sources, including translations from annotated coding regions in GenBank, RefSeq and TPA, as well as records from SwissProt, PIR, PRF, and PDB. BLAST finds regions of similarity between biological sequences.
#Amino acid sequence full#
De novo protein sequencing compiles multiple overlapping de novo peptide sequences to derive a full length protein sequence. mRNA codons are read from 5' to 3', and. Codons in an mRNA are read during translation, beginning with a start codon and continuing until a stop codon is reached. One 'start' codon, AUG, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine. In de novo peptide sequencing a the amino acid sequence of a peptide is determined via tandem mass spectrometry combined with bioinformatics algorithms, without a reference sequence or database. Three 'stop' codons mark the end of a protein. Use Protein Molecular Weight when you wish to predict the location of a protein of interest on a gel in relation to a set of protein standards. You can append copies of commonly used epitopes and fusion proteins using the supplied list.
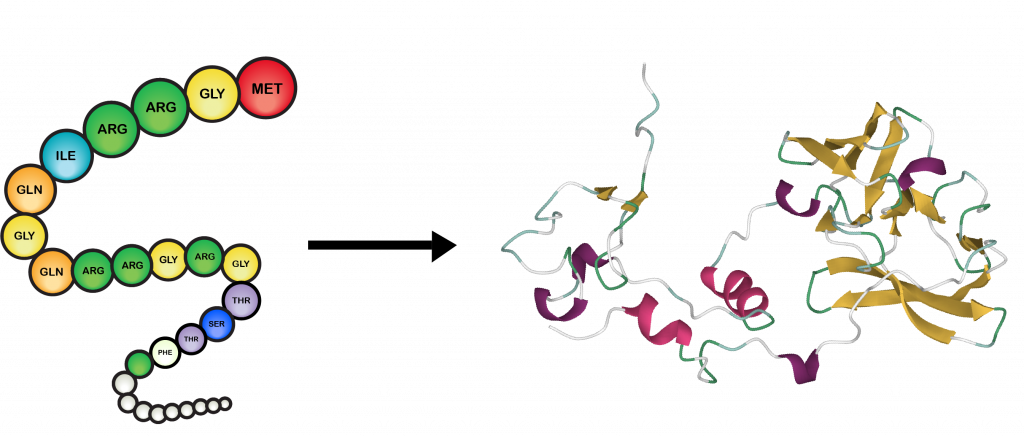
When a database or reference sequence is used, this is called protein identification, peptide sequence identification or peptide mapping. Protein Molecular Weight accepts a protein sequence and calculates the molecular weight. MS-based amino acid sequencing can be done with or without reference to a database of known sequences.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
